LIDARs
LIght Detection And Ranging
OVERVIEW
| Main Variants | Alternatives |
|---|---|
 | 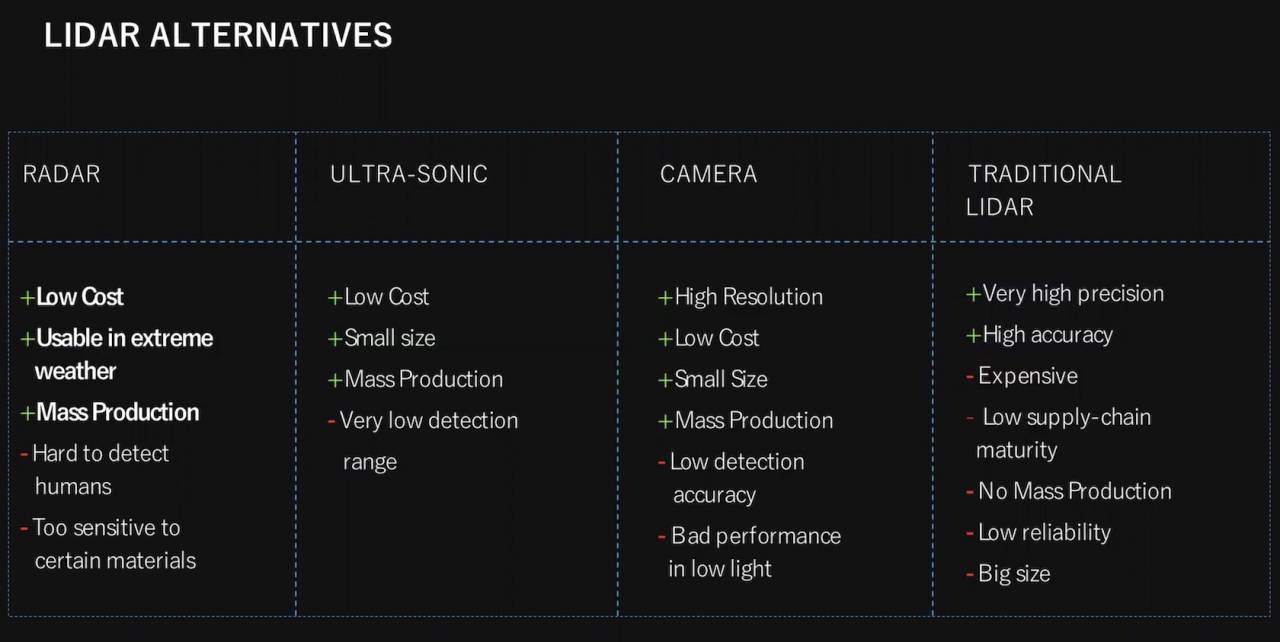 |
Sources of differences
A combination of all options leads to (~8k) LiDaRs:
- beam steering (9)
- Time of flight measurement (3)
- Optics (288)
Notes: beam steering (9): - Solid state (3) : none , DMD in TX, DMD in RX path - Rotating Mirrors (3) : polygon, galvano,
- Time of flight measurement (3): PMCW, FMCW, AMCW
- Optics (288):
- wavelength (4) : 850, 905, 940, 1550 nm
- Front-End dimensions (3) : (respectively #RX, #TX): 1x1, few x few, few x many
- Laser diode technology (2): edge emiting or VCSEL
- LD bias circuitry (2)
- Photo diode technology (3) : MPPC/SiPM, APD, Pin
- PD bias circuitry (2)
beam steering
- Non-mechanical (aka static or solid-state)
- Mechanical
Non-mechanical beam steering
- DMD (Digital Micro Mirror), a MEMS technology for controlling micro-mirrors
- can be on the TX side
- can be on the RX side
- Flash LiDaR - a very powerful Laser illuminates the entire scene and an array of photodetectors senses the return light.
- OPA - (Optical phase array) - In an OPA system, an optical phase modulator controls the speed of light passing through the lens.
Mecanical
- polygon-beam-scanners
- galvano scanner (polygon vs galvano)
- motorized with encoders
ToF measurement:
- PB-ToF (or PMCW): pulse based or pseudo-random sequences
- FMCW-ToF: Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave
- AMCW-ToF: Amplitude Modulated Contiuous Wave
PB-ToF (pulse based time of flight) or PMCW
- Simple version: simple pulse
- dual-slope or dual gate as in 1 - doi: 10.3390/s18061679 or 2 - doi=10.1.1.579.1245
- Advanced version - pseudorandom modulation continuous-wave (PMCW): with multiple pulse sent with a pseudo-random sequence.
FMCW-ToF
FMCW: Frequency Modulated Continuous Wave for Time of flight measurement
AMCW-ToF
Amplitude Modulated Continuous Wave Time of Flight
Notes:
Optics
- Wavelengthts
- Front-End dimensions
- Opto-electronics
Wavelengths
905nm and 1550nm are the dominant wavelength
| 850 | 905 nm | 940 nm | 1550 nm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pros | ||||
| Cons |
Front-End dimensions
- 1x1: single pixel TX, single pixel RX
- few x few : often multiple discrete LD and discrete LD
- few x many : eitehr 1x or few discrete LD and an integrated array of photos sensors
Laser diode
- Opto-electronic Technology
- Electronic bias circuitry (2)
## Photo diode * Opto-electronic Technology: - MPPC/SiPM - APD - Pin * Electronic bias circuitry (2)
Notes: p-i-n silicon detectors vs avalanche photodiodes or silicon photomultipliers CWFM-ToF can use coherent detection can be used with pin diodes which are significantly cheaper than APD often used in PB-ToF.
Atmospheric considerations
test: \(x_{1,2} = {-b\pm\sqrt{b^2 - 4ac} \over 2a}.\) some fundamentals \(P=P_0 * rho * A0/(pi*R2) *eta * exp(-2*gamma*R)\) Where:
- η0 is the detection optics’ spectral transmission,
- γ is the atmospheric extinction coefficient.
Back-up slides
Sources
- slashgear on lidar
- Forbes
- claims 468 variants of LiDaRs